Diopter/Sphere (D/dpt./PWR)

This value determines the power of the contact lens. Generally, spherical power is given in plus (+) values for farsightedness and minus (-) for nearsightedness. ATTENTION - the number of diopters of contact lenses may not match the diopters of your glasses.
Curvature (BC)

The curvature of the contact lens indicates the curvature of the eye in millimeters and thus also how closely the lens adheres to the eye. Usually this dimension is between 8-10 mm. Lower curvature, e.g. 8.40, means that the lens is more curved and will “fit“ more tightly on the eye. A higher curvature value, e.g. 8.70 means that the lens is more flat.
Diameter (DIA)

This value indicates the diameter (or size) of the lens. Soft contact lenses have a wider diameter than hard contact lenses.
Cylinder (CYL)

The cylinder value is important for making contact lenses for astigmatism. It describes the strength of astigmatism and has a minus value increasing in 0.25 increments that compensates for the curvature of the cornea.
Cylinder axis (AX)

The axis is the second important parameter in astigmatism. It indicates the exact position of curvature on the cornea in the range of 0° - 180°.
Addition (ADD)

Addition is the value given if you suffer from presbyopia. It is the difference between the dioptric value for distance and the dioptric value for near. Values up to 1.25 are considered low (also referred to as “low“), up to 2.00 as average (“medium“) and until 3.00 for high (“high“).
No customer reviews yet - try the product and share your experience.
AIROPT ASTG HG 3
Package size
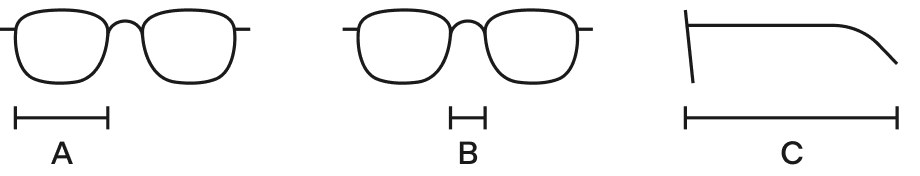
TIP #1: Check the size of your current glasses
- Look at the inside of your glasses. Usually you´ll find a series of numbers there that represent the frame size and look something like this: 52 [] 22 145
- Information about the size of the frame is most often found on the inside of the temples

TIP #2: Use a payment card



Dimensions of frames
You forgot to select diopters

Select according to the plus (+) or minus (-/=) values from your eye doctors prescription.
Diopter/Sphere (D/dpt./PWR)

This value determines the power of the contact lens. Generally, spherical power is given in plus (+) values for farsightedness and minus (-) for nearsightedness. ATTENTION - the number of diopters of contact lenses may not match the diopters of your glasses.
Curvature (BC)

The curvature of the contact lens indicates the curvature of the eye in millimeters and thus also how closely the lens adheres to the eye. Usually this dimension is between 8-10 mm. Lower curvature, e.g. 8.40, means that the lens is more curved and will “fit“ more tightly on the eye. A higher curvature value, e.g. 8.70 means that the lens is more flat.
Diameter (DIA)

This value indicates the diameter (or size) of the lens. Soft contact lenses have a wider diameter than hard contact lenses.
Cylinder (CYL)

The cylinder value is important for making contact lenses for astigmatism. It describes the strength of astigmatism and has a minus value increasing in 0.25 increments that compensates for the curvature of the cornea.
Cylinder axis (AX)

The axis is the second important parameter in astigmatism. It indicates the exact position of curvature on the cornea in the range of 0° - 180°.
Addition (ADD)

Addition is the value given if you suffer from presbyopia. It is the difference between the dioptric value for distance and the dioptric value for near. Values up to 1.25 are considered low (also referred to as “low“), up to 2.00 as average (“medium“) and until 3.00 for high (“high“).